Project Business Automation (PBA) is a business process management software designed for project-driven business that integrates all core project business processes into one, end-to-end system. PBA is considered a specialized project business system that streamline project management processes by standardizing, integrating, and automating them within a single unified platform. PBA is now recognized by Forrester as the next category of software solutions for project-driven organizations.
This comprehensive solution effectively tackles the complexities of project management for enterprises, providing the financial and operational tools, controls, and insight to optimize the project lifecycle across the organization.
Key Components of Project Business Automation
PBA provides an integrated and continuously updated view of core project business processes normally managed in disparate applications. These core processes can be categorized in 3 main functional areas:
- Project Financials and Accounting
- Project Management and Operations
- Project Insight and Analytics
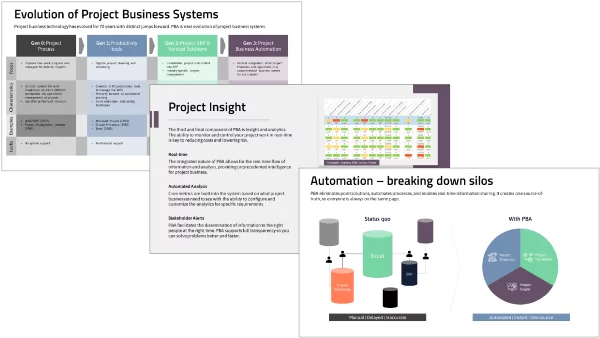
The key point about PBA is that all these areas are integrated in one system, providing real-time data streams that facilitate the acceleration and automation of processes that is not possible when managed in separate applications.
Project Financials and Accounting – This area of PBA covers the financial management of projects and portfolios of projects. It includes, at a minimum, project costing, cost breakdown structures, budget management, estimate-at-completion, budget-at-completion, cost-to-complete, month-end reporting, cash flow management, revenue projections and revenue recognition. These functions are normally managed in the ERP, other accounting applications and various spreadsheets.
Project Management and Operations – This area of PBA covers the operational component of projects. It includes, at a minimum, work breakdown structures, project scheduling, risk and issue management, milestone management, resource management, subcontract management. These functions are normally managed in project management/planning/scheduling applications, custom-built applications and various spreadsheets.
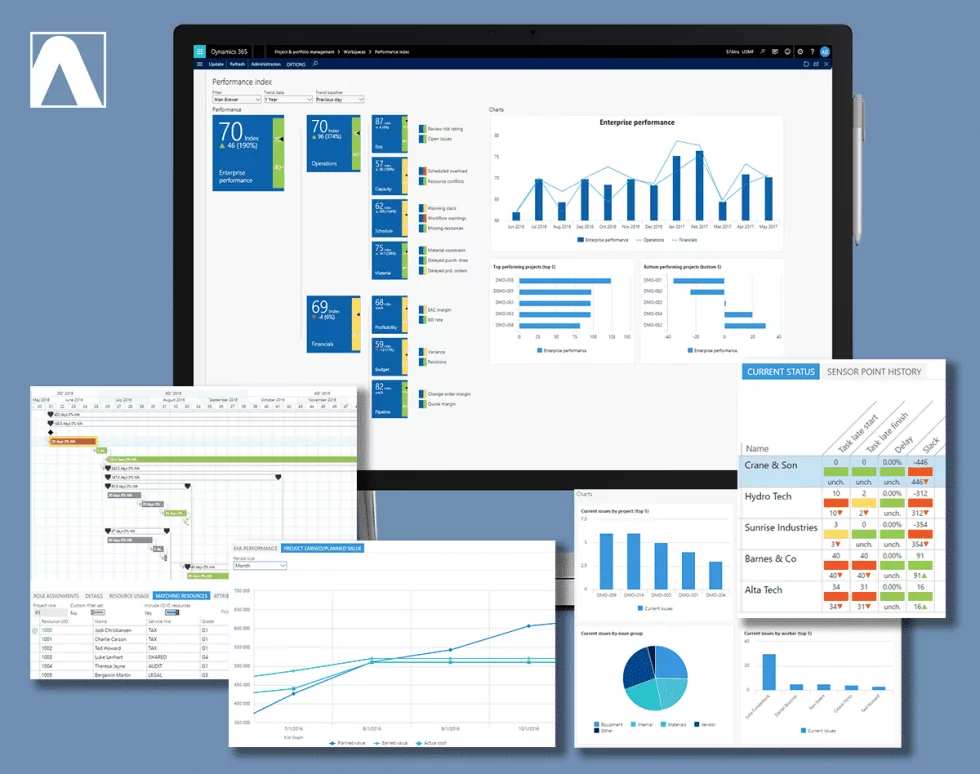
Project Insight and Analytics – This area of PBA covers the real-time analysis of projects, portfolios and the business as whole. Since all functional areas are integrated, PBA produces time-phased operational and financial threshold data, giving project-driven organizations the ability to run their projects with real-time visibility and control over processes, costs and risks. It includes real-time metrics such as cash flow, margins, estimate-at-completion, earned value analysis, and variances on several key performance indicators in operations and finance. These types of analyses are normally produced infrequently in spreadsheets and separate BI applications, and therefore not in real-time.
Download the Project Business Automation Quick Guide to learn more about PBA
Integrating with PBA
PBA should be self-contained and be able to summarize and exchange critical information with your ERP. The ability to easily integrate with your ERP ensures consistent and automated workflows across your business. This approach gives you the best-of-breed approach by providing a state-of-the-art project business system while connecting with the rest of your business to ensure stability.
Origin of the term Project Business Automation
The term Project Business Automation was first used by Adeaca in 2019. It married the terms Project Business, first used by Karlos A. Artto and Kim Wikström in a research article published in the International Journal of Project Management in 2005, and Automation to represent the systemization of the former.
In this context, Project Business is used to represent all project-based organizations, companies that conduct projects as their primary mode of delivering their goods and services to their customers. These businesses include construction, engineering, architecture, ETO/project manufacturing, and other professional services.
The market need for PBA grew out of the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) industry. While ERP is a viable solution for most traditional enterprises in manufacturing, retail, distribution, etc., it did very little to encompass the process management needs of Project Business. As a result, most Project Businesses use many other applications to manage the core of their business processes, which revolve around projects.
Project Business Automation manages all those processes in one system, essentially creating a viable ERP alternative for project-based companies.